01 / 16
2019
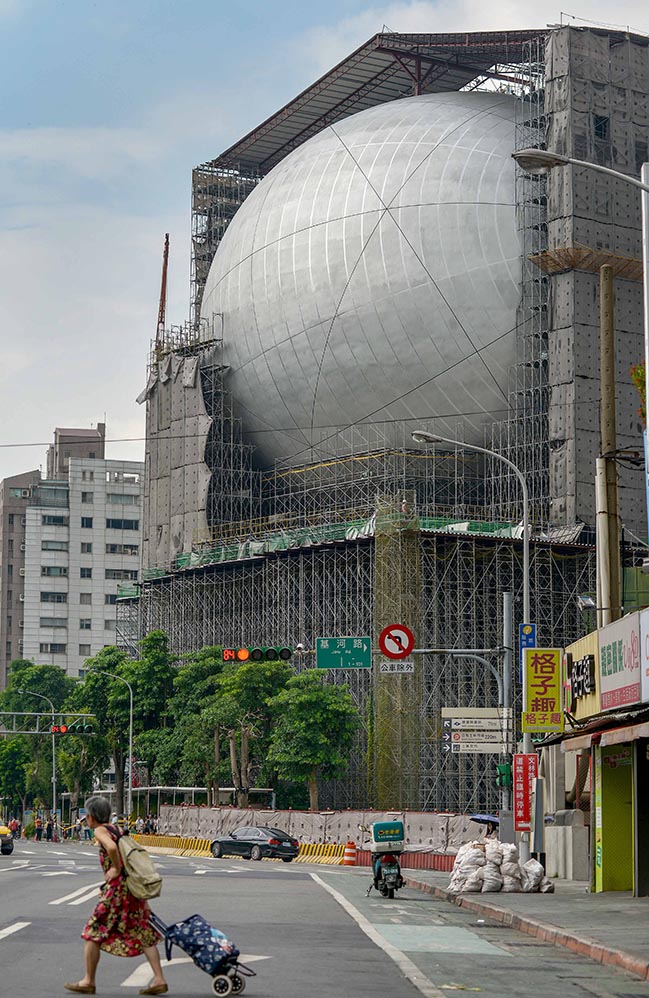
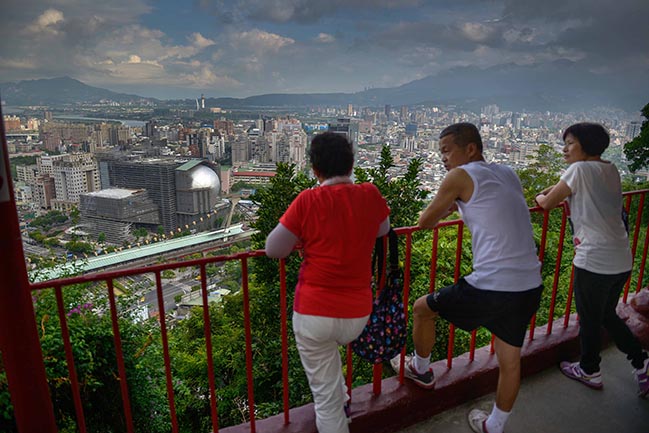
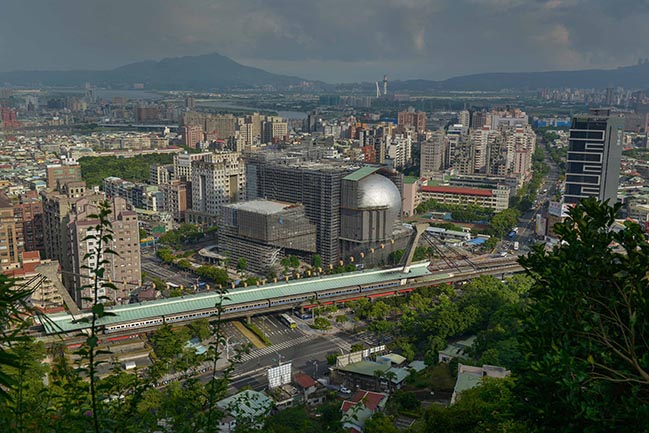
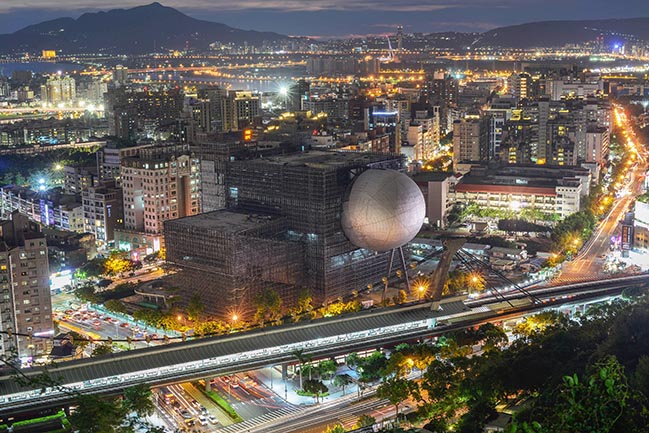
The Office for Metropolitan Architecture (OMA) has updated new photos of the Taipei Performing Arts Center (TPAC) which is nearing completion.
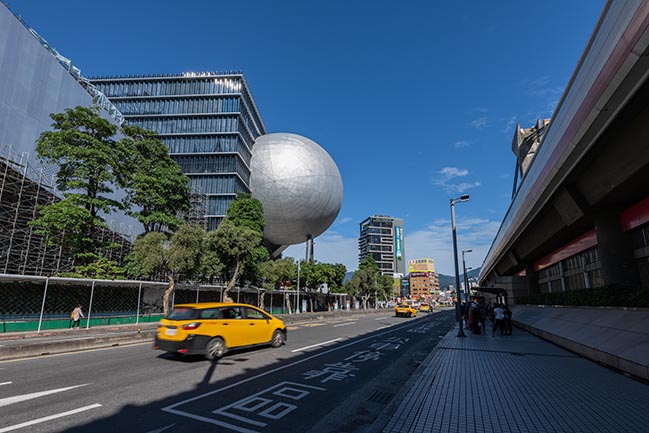

Photograph by Kevin Mak, Courtesy of OMA
Architect: OMA
Client: Department of Cultural Affairs, Taipei City Government
Location: Taipei, Taiwan
Partners-in-charge: Rem Koolhaas, David Gianotten
Associate-in-charge: Adam Frampton
Design team: Ibrahim Elhayawan with: Yannis Chan, Hin-Yeung Cheung, Jim Dodson, Inge Goudsmit, Alasdair Graham, Vincent Kersten, Chiaju Lin, Vivien Liu, Kai Sun Luk, Kevin Mak, Slobodan Radoman, Roberto Requejo, Saul Smeding, Elaine Tsui, Viviano Villarreal, Casey Wang, Leonie Wenz
Competition team: partners / designers: Rem Koolhaas, David Gianotten, Ole Scheeren, and senior architects: André Schmidt, Mariano Sagasta and Adam Frampton, with: Erik Amir, Josh Beck, Jean-Baptiste Bruderer, David Brown, Andrew Bryant, Steven Chen, Dan Cheong, Ryan Choe, Antoine Decourt, Mitesh Dixit, Pingchuan Fu, Alexander Giarlis, Richard Hollington, Shabnam Hosseini, Sean Hoo , Takuya Hosokai, Miguel Huelga, Nicola Knop, Chiaju Lin, Sandra Mayritsch, Vincent McIlduff, Alexander Menke, Ippolito Pestellini, Gabriele Pitacco, Shiyun Qian, Joseph Tang, Agustin Perez-Torres, Xinyuan Wang, Ali Yildirim, Patrizia Zobernig
NEW PHOTOS 2018
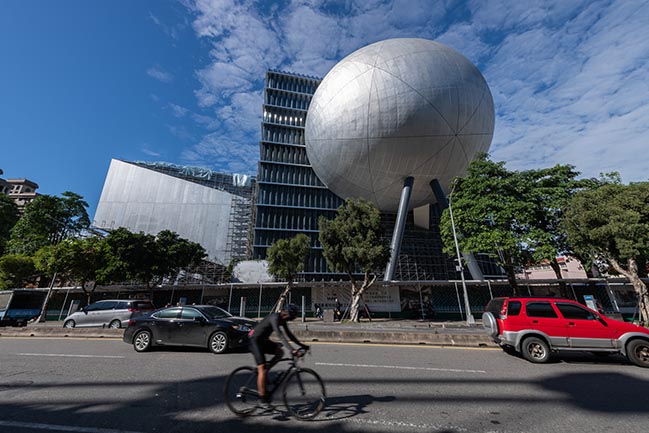

Photograph by Kevin Mak, Courtesy of OMA
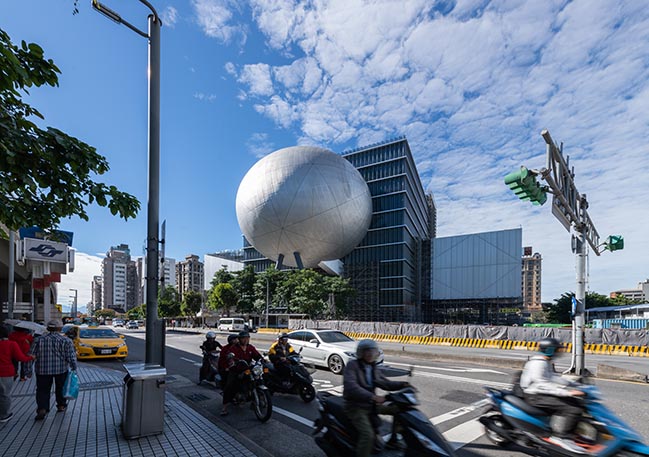

Photograph by Kevin Mak, Courtesy of OMA
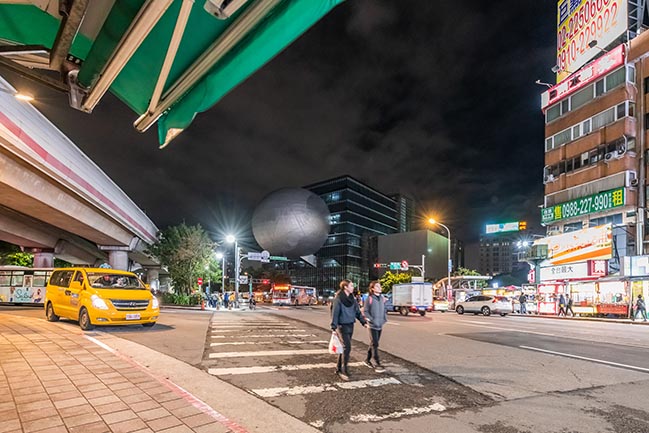

Photograph by Kevin Mak, Courtesy of OMA
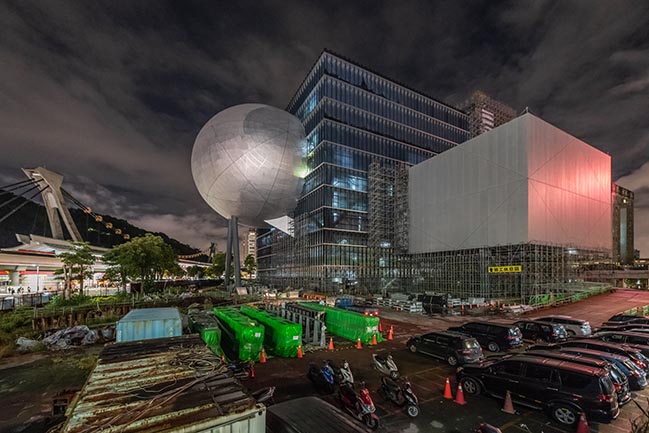

Photograph by Kevin Mak, Courtesy of OMA
Project description: Why have the most exciting theatrical events of the past 100 years taken place outside the spaces formally designed for them? Can architecture transcend its own dirty secret, the inevitability of imposing limits on what is possible?
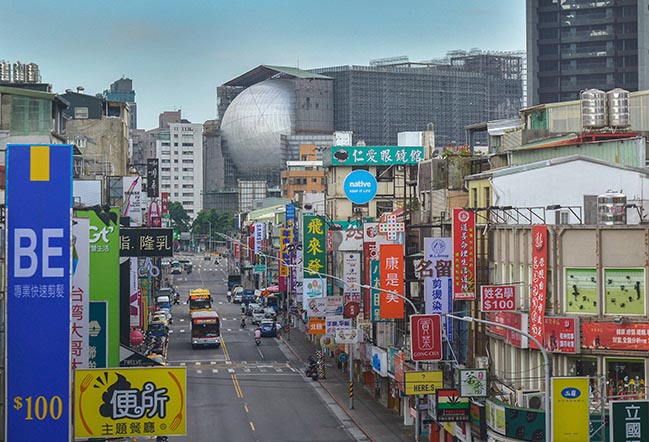

© OMA by Chris Stowers
In recent years, the world has seen a proliferation of performance centres that, according to a mysterious consensus, consist of more or less an identical combination: a 2,000-seat auditorium, a 1,500-seat theatre, and a black box. Overtly iconic external forms disguise conservative internal workings based on 19th century practice (and symbolism: balconies as evidence of social stratification). Although the essential elements of theatre– stage, proscenium, and auditorium– are more than 3,000 years old, there is no excuse for contemporary stagnation. TPAC takes the opposite approach: experimentation in the internal workings of the theatre, producing (without being conceived as such) the external presence of an icon.
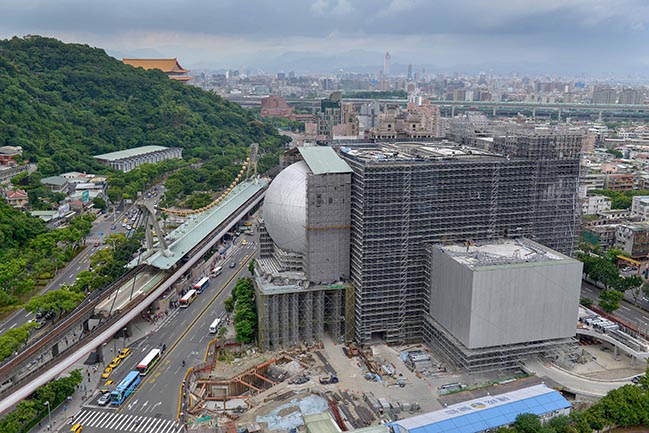

© OMA by Chris Stowers
TPAC consists of three theatres, each of which can function autonomously. The theatres plug into a central cube, which consolidates the stages, backstages and support spaces into a single and efficient whole. This arrangement allows the stages to be modified or merged for unsuspected scenarios and uses. The design offers the advantages of specificity with the freedoms of the undefined.

© OMA by Chris Stowers
Performance centres typically have a front and a back side. Through its compactness, TPAC has many different “faces,” defined by the individual auditoria that protrude outward and float above this dense and vibrant part of the city. The auditoria read like mysterious, dark elements against the illuminated, animated cube that is clad in corrugated glass. The cube is lifted from the ground and the street extends into the building, gradually separating into different theatres.

© OMA by Chris Stowers
The Proscenium Playhouse resembles a suspended planet docking with the cube. The audience circulates between an inner and outer shell to access the auditorium. Inside the auditorium, the intersection of the inner shell and the cube forms a unique proscenium that creates any frame imaginable.

© OMA by Chris Stowers
The Grand Theatre is a contemporary evolution of the large theatre spaces of the 20th century. Resisting the standard shoebox, its shape is slightly asymmetrical. The stage level, parterre, and balcony are unified into a folded plane. Opposite the Grand Theatre on the same level, the Multiform Theatre is a flexible space to accommodate the most experimental performances.

© OMA by Chris Stowers
The Super Theatre is a massive, factory-like environment formed by coupling the Grand Theatre and Multiform Theatre. It can accommodate the previously impossible ambitions of productions like B.A. Zimmermann’s opera Die Soldaten (1958), which demands a 100-metre-long stage. Existing conventional works can be re-imagined on a monumental scale, and new, unimagined forms of theatre will flourish in the Super Theatre.
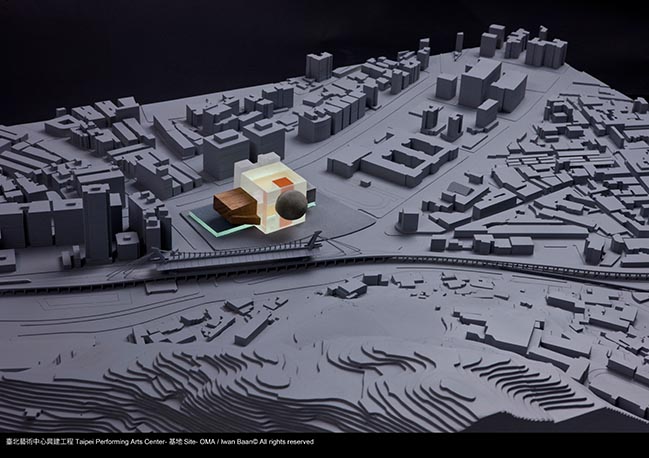

By Iwan Baan © OMA
The general public—even those without a theatre ticket—are also encouraged to enter TPAC. The Public Loop is trajectory through the theatre infrastructure and spaces of production, typically hidden, but equally impressive and choreographed as the “visible” performance. The Public Loop not only enables the audience to experience theatre production more fully, but also allows the theatre to engage a broader Public.
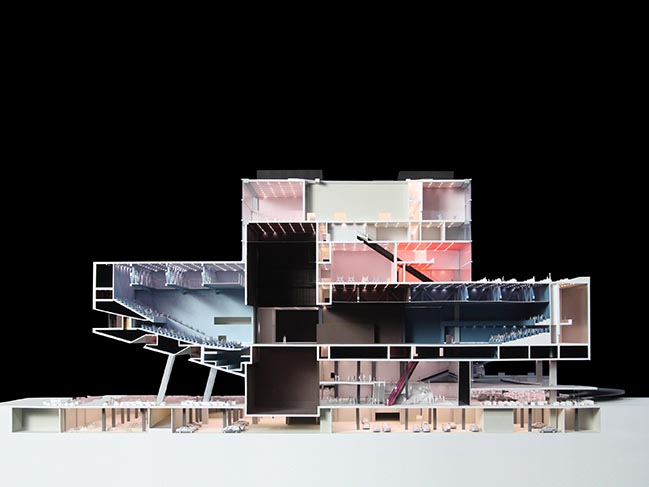

By Frans Parthesius © OMA
COLLABORATORS
Local architect: Artech Architects
Theatre consultant: dUCKS scéno, CSI
Interior designer: Inside Outside
Landscape designer: Inside Outside
Acoustic consultant: DHV
Structural engineer: Arup Structure, Evergreen
MEP engineer: Arup MEP, Heng Kai, IS Lin
Fire engineer: Arup Fire, TFSC
Lighting consultant: Chroma 33
Facade engineer: ABT, CDC
Sustainability consultant: Arup Building Physics, Segreene
Geotechnical engineer: Sino Geotech
Traffic consultant: EECI Traffic
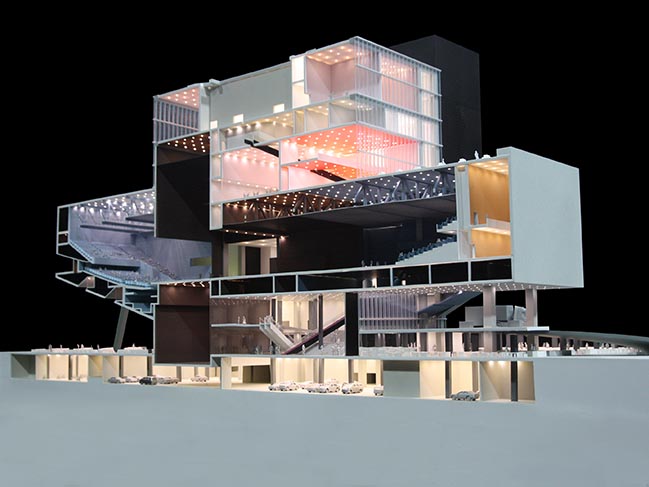

By Frans Parthesius © OMA
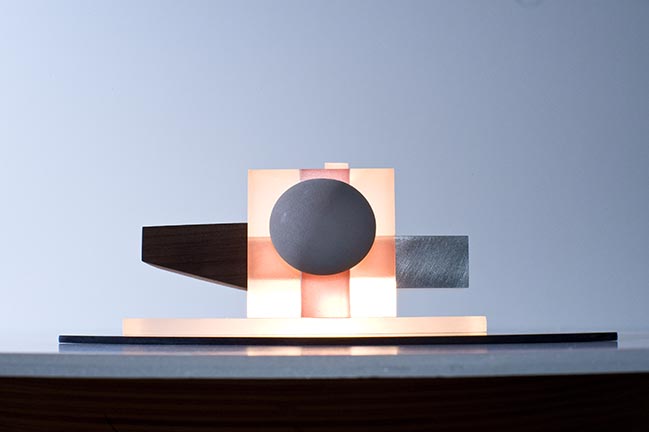
By Frans Parthesius © OMA
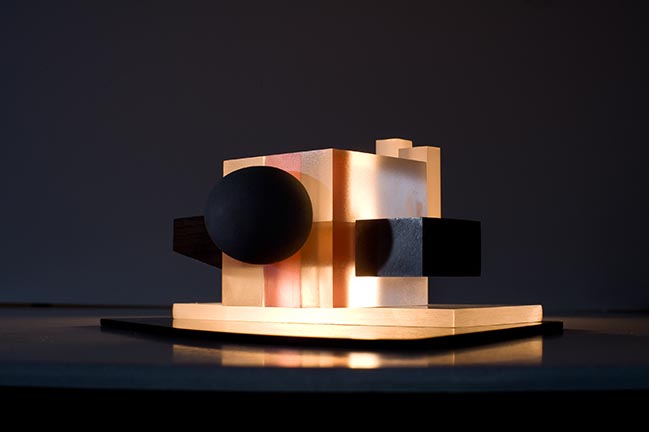

By Frans Parthesius © OMA
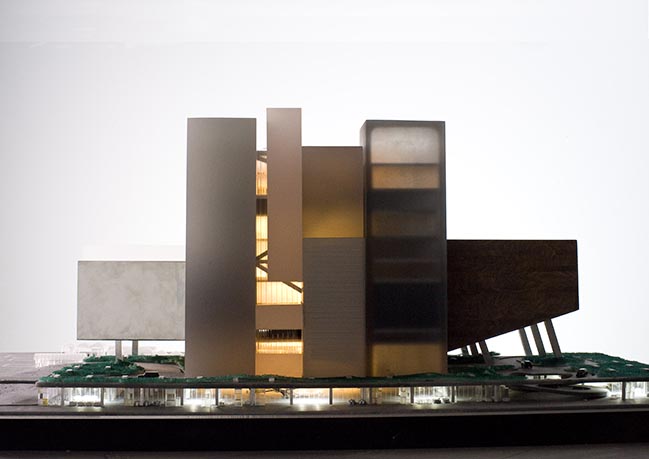

By Frans Parthesius © OMA
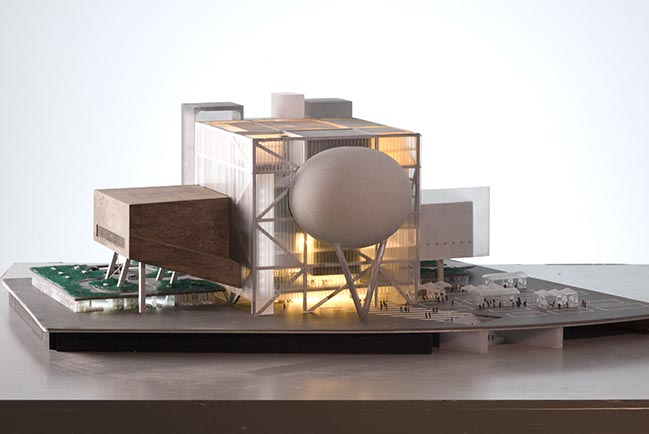

By Frans Parthesius © OMA
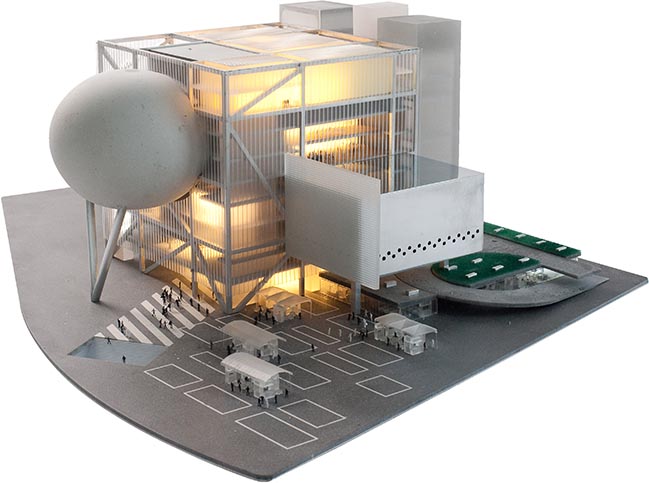
By Frans Parthesius © OMA
New photos of OMA's Taipei Performing Arts Center
01 / 16 / 2019 The Office for Metropolitan Architecture (OMA) has updated new photos of the Taipei Performing Arts Center (TPAC) which is nearing completion
You might also like:
Recommended post: Stade de Luxembourg by gmp Architekten opened




















